In the course of consulting and supporting customers, Maxserver has receive many questions about RAID. So what is RAID? What does RAID function? What types of RAID? What are advantages and disadvantages of each type? To a specific service which type of RAID should be used to reach the optimum level?
To explore RAID we should know what RAID is
RAID (Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks) is a form of combining many physically hard discs into a system of hard disks which can increase the data reading/recording speed or enhance the security of data stored in the disc system or both of these two
Many types of RAID are used such as Raid 0, Raid 1, Raid 3, Raid 4, Raid 5, Raid 10 .v.v… In this post Maxserver will introduce four main types of RAID which are commonly-used by our customers, they are Raid 0, Raid 1, Raid 10 và Raid 5.
1. RAID 0:
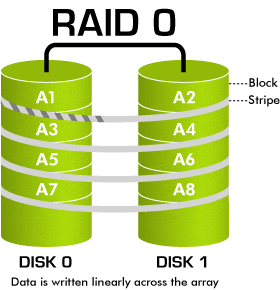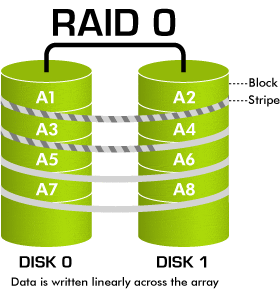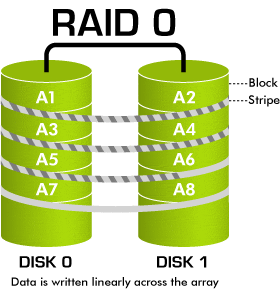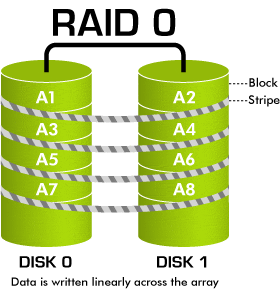
Raid 0 is quite commonly-used today because of its ability to increase the efficiency and the speed of hardware reading and recording data. Setting up RAID 0 requires at least 2 disks (Disk 0, Disk 1).
File A will be saved as follows: Suppose you have 1 file A with 100MB of storage, in the process of saving, file A will not be saved in only one hardware, RAID 0 helps save it in 2 disks, disk 0 and disk 1 each with 50MB of storage(Striping) This helps decrease half of the theoretic reading time
Advantage: Reading speed faster (double it theoretically)
Disadvantage: potential data risks. The data is divided to be saved in 2 disks.In case 1 of the 2 disks gets down the possibility of losing data will be great. Hardwares need to have the same storage level, if they are different you pick the smaller one
Use for: suitable for services that need high speed of saving and access. For example video streaming, PTU, Render, etc (In this form of saving MaxServer recommend customers to backup your data
2. RAID 1:

Raid 1 is a fundemental RAID which is commonly-used today for its data security. Setting up RAID 1 is similar to RAID 0, requiring at least 2 hardwares
Unlike RAID 0, RAID 1 ensures greater security because the data is save in 2 identical hardwares (Mirroring).
Advantage: Safe for data. In case 1 out of 2 disks gets down, data still meets the service demand
Disadvantage: Low efficiency, cost more (suppose you use 2 hardwares of 500GB, the space available to use is only 500GB). 2 hardwares with the same storage level are required, if they are different then pick the smaller one
Use for: Saving services, medium and small websites do not require hardware high reading and recording (in/out) speed. These services need the security of data such as accounting, customer information management, real estate, etc
3. RAID 10:

Raid 10 is a combination of 2 common types of RAID which are RAID 1 and RAID 0. Setting up RAID 10 requires at least 4 hardwares (Disk 0, Disk 1, Disk 2, Disk 3).
When it comes to RAID 10, data is saved simultanously in 4 hardwares: 2 of which in the form of Striping (Raid 0) and the other 2 in the form of Mirroring (Raid 1).
Advantage: This is a fast and safe way of saving, both increasing the efficiency and preventing data loss in case 1 out of 4 hardwares gets down
Disadvantage: High cost. To RAID 10 the available space to use only accounts for 1/2 the total space of 4 hardwares (like raid 1).
Use for: Raid 10 is suitable for all subjectsthích hợp với tất cả các đối tượng sử dụng (from needs for the efficiency to the data security). 4 hardwares with the same storage level are required, if they are different then pick the smallest
4. RAID 5:

Raid 5 is quite a widely-used type of RAID. Basic rules of RAID 5 is similar to 2 traditional types which are RAID 1 and RAID 0. This means the data will also be saved in 2 seperated hardwares and a providing option in case there is any problem that occurs to one of the hardwares
Setting up RAID 5 requires at least 3 hardwares. According to the illustration, the option of RAID 5 is that: Suppose there is a file A during saving which is divided into 3 parts A1, A2, A3. These 3 parts are saved in Disk 0, Disk 1, Disk 2 respectively. Disk 3 will store the backup of these 3. It is similar to next files. Depending on every stage the progress, the backup will be saved in one of the hardwares in RAID
Advantage: Increase the efficinecy, ensure data security, cost less than RAID 10
Disadvantage: an extra hardware costs more than the ordinary way of saving (eventually the total space of hardwares will be the total space of used disks substracting one hardware. Suppose you have 4 hardwares with 500GB, the last space after proceeding RAID 5 will be 1500GB).
Use for: All websites, services and applications with the amount of access and the need for resources from small to medium to large size
These are fundamental definitions about some commonly-used types of RAID. You can get a preference and pick the most suitable type of RAID for your need. If there is any question please contact MaxServer to get more support